
Geography of Haiti
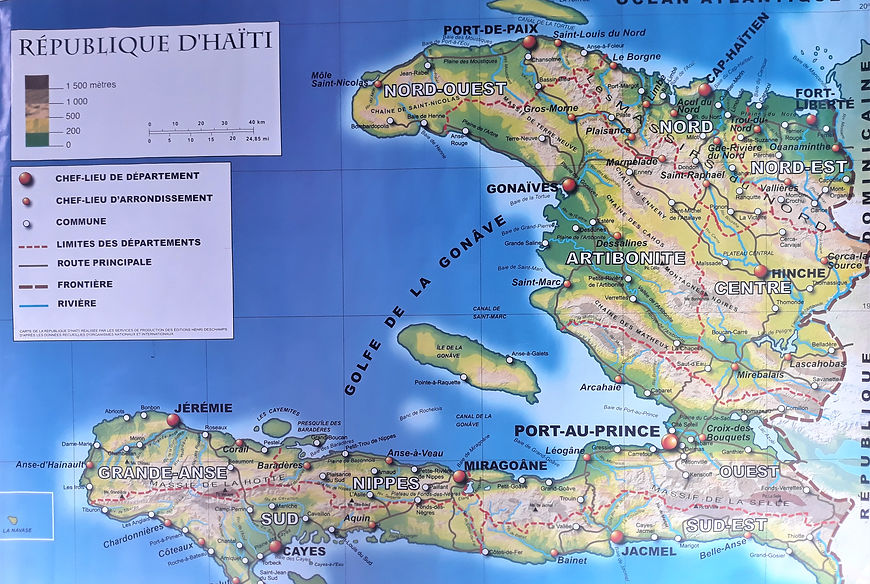
Located east of Cuba and 190 km northeast of Jamaica, the Republic of Haiti occupies the western third of the island of Haiti (former Santo Domingo), bathed, to the north, by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the Antilles (or Caribbean) Sea.
It is a country with a tropical climate, formed by mountain ranges, the highest point of which is the Pic de la Selle, 2680m above sea level, some plains, valleys and high plateaus with a coastline of more than 1500 km, where live near of 12 million inhabitants, on an area of 27,750 km² with a density of 428 h / km². More than 50% of the territory is made up of slopes of more than 40%. The languages are Creole and French. The currency is the gourde but the American dollar remains a very strong currency and used in the economic system.
The Republic of Haiti is divided into 10 departments and 42 districts made up of 140 communes and 570 communal sections. The capital is Port-au-Prince, in the western department.
Religion: 50% Catholic, nearly 45% Protestant, but the practice of voodoo remains dominant.
The natural resources of the Haitian subsoil are very rich (bauxite, gold, petroleum, iridium,…), but not exploited and under the covetousness of foreign companies.
The economy is predominantly agricultural but the lack of cultivable land is a fundamental problem, the deforestation of the mountains, causing the acceleration of erosion and the disappearance of soils, has taken on the appearance of a real national disaster.
The clearing of new lands and the accelerated production of charcoal are causing the rapid decline of the forest, which covers only less than 2% of the country's surface. In the 15th century, it is estimated that 80% of the island was forested and in 1923, almost 60% of the country.
Two-fifths of Haitians depend on the agricultural sector, mainly small subsistence farms, and remain vulnerable to frequent natural disasters exacerbated by deforestation . Fishing remains very archaic. The agricultural sector contributes only 45% of the country's food needs.
The number of Haitians in a situation of food insecurity exceeds four and a half million.
Life expectancy is 63.3 years (World Bank, 2016)
The literacy rate is 48.68% (UNDP, 2005-2013), access to education remains very limited.
The human development indicator is one of the lowest in the world, three quarters of the population live on less than two dollars a day.
Debt is overwhelming, and unemployment affects at least 60% of the working population. Informal activities are plentiful. Contraband, which represents more than 20% of the value of Haitian imports, remains a lucrative activity.
Haiti must rely on funds from the diaspora (20% of GDP) and on international aid to survive.
Two thirds of Haitians are affected by unemployment or underemployment.
The main suppliers are the United States (27%) and the Dominican Republic (35%).
The share of the main sectors of activity in GDP (World Bank, 2017) are:
-
agriculture: 17.58%
-
industries: 56.77%
-
services: 25.65%
According to the latest IMF ranking, for 2021, Haiti is the 15th poorest country in the world with a GDP of 697 usd / capita.
By comparison, Nicaragua is the second poorest country in the Americas, with a GDP of 2029 usd / capita, almost 3 times more than Haiti. The Dominican Republic, the neighbor, has a GDP of 7.650 Usd / capita, almost 11 times more than Haiti.
The country is characterized by bad governance and corruption and totalitarian abuses.

